

The occurrence of a TIA is a risk factor for having a major stroke, and many people with TIA have a major stroke within 48 hours of the TIA.
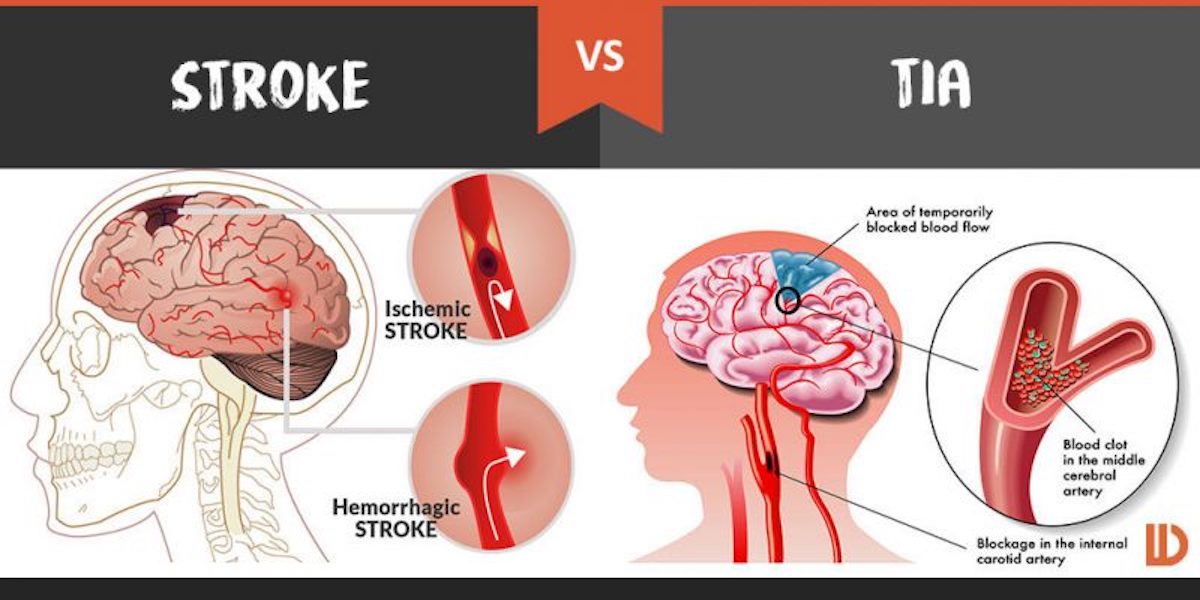
The same person can have major strokes, minor strokes, and silent strokes, in any order. In silent stroke, also known as silent cerebral infarct (SCI), there is permanent infarction detectable on imaging, but there are no immediately observable symptoms. While a TIA must by definition be associated with symptoms, strokes can also be asymptomatic or silent. The primary difference between a major stroke and the TIA's minor stroke is how much tissue death ( infarction) can be detected afterwards through medical imaging. A TIA is caused by a temporary disruption in blood flow to the brain, or cerebral blood flow (CBF).

TIA causes the same symptoms associated with strokes, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, sudden dimming or loss of vision, difficulty speaking or understanding language, slurred speech, or confusion.Īll forms of stroke, including TIA, result from a disruption in blood flow to the central nervous system. Survival rate ~ 91% (to hospital discharge) 67.2% (five years) Ī transient ischemic attack ( TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, is a minor stroke whose noticeable symptoms usually end in less than an hour. doi: 10.1002/ condition Transient ischemic attack A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of miR-155 predicts the risk of intracranialhemorrhage caused by rupture intracranial aneurysm. Yang X, Peng J, Pang J, Wan W, Chen L.Risk factors predicting a higher grade of subarachnoid haemorrhage in small ruptured intracranial aneurysm (< 5 mm). Tai J, Liu J, Lv J, Huibin K, Hou Z, Yang J et al.The PHASES score: to treat or not to treat? Retrospective evaluation of the risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Pagiola I, Mihalea C, Caroff J, Ikka L, Chalumeau V, Iacobucci M et al.Juvela S.Treatment Scoring of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms.The Merck Manuals: Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Cedars-Sinai Medical Center: Cerebral Aneurysms and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.National Institutes of Health: Brain Aneurysm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
